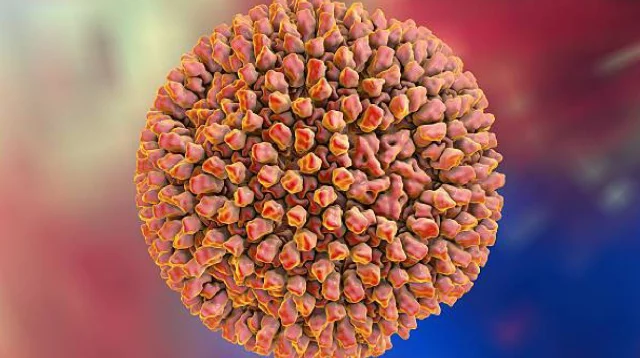
Reovirus (short for Respiratory Enteric Orphan Virus) is a genus of viruses known to infect a wide range of organisms, including humans. While reoviruses are generally considered mild or even asymptomatic in most cases, they can sometimes cause notable illness, particularly in specific populations such as infants, immunocompromised individuals, or animals.
Here’s a detailed overview of symptoms, treatment, and risks associated with reovirus infections:
Symptoms of Reovirus Infection
In humans, reovirus infections are often asymptomatic or produce mild symptoms because the virus is typically non-pathogenic. When symptoms do occur, they are often associated with respiratory or gastrointestinal systems. Here’s a breakdown:
Respiratory Symptoms:
- Mild upper respiratory infections resembling the common cold.
- Runny nose, sneezing, and nasal congestion.
- Sore throat and mild cough.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms:
- Diarrhea (common in infants and young children).
- Nausea and occasional vomiting.
- Mild abdominal discomfort or cramps.
Systemic Symptoms (Less Common):
- Fever (low-grade or moderate).
- Fatigue and malaise.
- Rarely, a rash or muscle pain.
Complications (Rare):
In individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying conditions, reovirus may lead to:
- Severe diarrhea and dehydration (in young children).
- Chronic infections, especially in people undergoing chemotherapy or organ transplants.
- Possible links to more severe neurological symptoms, though rare, such as encephalitis or meningitis.
How Dangerous Is Reovirus?
In general, reovirus is not highly dangerous for the majority of healthy individuals. However, its level of severity can vary:
- In Infants and Young Children:
- Infants are particularly prone to gastrointestinal symptoms, which can lead to dehydration if not managed promptly.
- The virus may resemble rotavirus infections in children, although reovirus tends to be less severe.
- In Immunocompromised Individuals:
- People with weakened immune systems may experience prolonged or more severe symptoms.
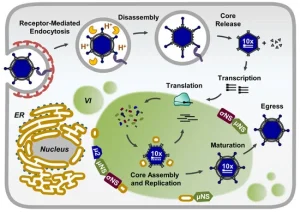
- Complications, though uncommon, can include persistent infection or systemic spread.
- People with weakened immune systems may experience prolonged or more severe symptoms.
- Potential Role in Cancer:
- Interestingly, reovirus is being studied for its potential connection to certain cancers. It can preferentially replicate in cancer cells with mutated Ras pathways, a mechanism that has led to its exploration as a therapeutic oncolytic virus. This makes the virus less of a danger and more of a research interest in oncology.
- Animal Health Concerns:
- In animals, reovirus infections can sometimes cause significant illness, particularly in poultry and livestock, leading to economic concerns in farming industries.
Treatment Options
Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment for reovirus infections in humans. Management is generally supportive and focuses on relieving symptoms:
For Respiratory Symptoms:
- Over-the-counter decongestants, antihistamines, or throat lozenges.
- Plenty of fluids and rest to boost recovery.
For Gastrointestinal Symptoms:
- Rehydration is key—oral rehydration solutions (ORS) or electrolyte-rich fluids can help.
- In severe cases of diarrhea, hospitalization for IV fluids might be necessary.
General Supportive Care:
- Fever reducers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can manage fever and discomfort.
- Good nutrition to support the immune system.
- Avoidance of irritants like tobacco smoke or heavy pollution.
For High-Risk Groups:
- Immunocompromised patients may require close monitoring to prevent complications.
- In severe cases, doctors may prescribe broad-spectrum antivirals, though they are not specifically approved for reovirus.
Prevention
Preventive measures are largely focused on reducing the transmission of the virus:
- Hygiene Practices:
- Wash hands regularly, especially after using the restroom or handling diapers.
- Clean and disinfect surfaces, particularly in shared environments.
- Wash hands regularly, especially after using the restroom or handling diapers.
- Safe Food and Water:
- Ensure proper sanitation to prevent fecal-oral transmission.
- Avoid contaminated food or water sources.
- Protect Vulnerable Populations:
- Keep infected individuals away from infants or those with weakened immune systems.
- Encourage breastfeeding in infants, as maternal antibodies may provide some protection.
How Reovirus Fits in the Viral Landscape
Reovirus is not a virus that should cause widespread fear. It belongs to a group of “orphan” viruses, meaning it was initially thought not to be associated with any diseases in humans. Its ability to cause mild illness or remain entirely unnoticed makes it less concerning than viruses like rotavirus, norovirus, or adenovirus, which are known for more aggressive symptoms.
However, the intriguing role of reovirus as a tool in cancer therapy highlights its unique nature. Researchers are actively studying how reovirus can be harnessed as a biological weapon against tumors due to its ability to exploit certain cellular mutations.
Key Takeaways
- For most people, reovirus infection is mild and self-limiting, with symptoms that resemble a cold or a mild stomach bug.
- Populations at higher risk—infants, the elderly, and the immunocompromised—should take precautions to avoid complications.
- Supportive care, hydration, and good hygiene are the mainstays of managing reovirus infections.
- Despite its minimal danger in most cases, reovirus’s potential in cancer treatment adds a fascinating dimension to its study.
Would you like more details on its connection to cancer research or animal health? Let me know!



 DailyMediCure
DailyMediCure