Low testosterone (low T) can lead to a variety of physical, emotional, and sexual symptoms. These can affect both men and women, but low testosterone is most commonly associated with men. Here are some common symptoms:
Physical Symptoms:
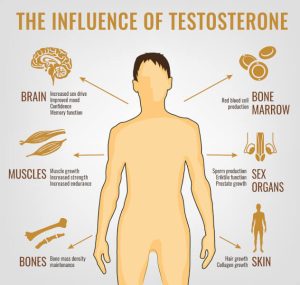
- Reduced Muscle Mass and Strength: Testosterone plays a key role in muscle development and strength. Low levels may lead to decreased muscle mass.
- Increased Body Fat: Low testosterone can lead to a rise in body fat, particularly around the abdomen.
- Fatigue and Decreased Energy Levels: A lack of testosterone may cause persistent fatigue and a general lack of energy.
- Reduced Bone Density: Testosterone helps maintain bone density, and low levels can increase the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
- Hot Flashes: Similar to the symptoms experienced by women during menopause, men with low testosterone may experience hot flashes.
- Sleep Problems: Difficulty sleeping or experiencing disrupted sleep (including insomnia or sleep apnea) may be related to low T.
- Hair Loss: Testosterone affects hair growth, and low levels may contribute to a decrease in body or facial hair.
- Decreased Libido: Low testosterone can cause a reduced sex drive (libido) and difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
- Reduced Motivation or Depression: Low testosterone can lead to feelings of sadness, depression, or a lack of motivation.
Emotional and Cognitive Symptoms:
- Irritability or Mood Swings: Testosterone influences mood, and low levels may cause irritability, mood swings, or feelings of sadness.
- Difficulty Concentrating or Memory Problems: Testosterone plays a role in cognitive function, and low levels may affect focus, memory, and mental clarity.
How to Increase Testosterone Levels Long-Term:
- Healthy Diet:
- Balanced Nutrition: Ensure a diet rich in healthy fats, lean proteins, and complex carbohydrates. Foods such as avocados, eggs, olive oil, and nuts support hormone health.
- Zinc and Vitamin D: Zinc is essential for testosterone production, found in foods like meat, shellfish, and legumes. Vitamin D, often gained through sunlight exposure or supplementation, also helps maintain testosterone levels.
- Regular Exercise:
- Strength Training: Weightlifting and resistance training can help boost testosterone levels by promoting muscle growth.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Short bursts of intense exercise can elevate testosterone and improve overall health.
- Avoid Overtraining: While exercise is beneficial, excessive physical stress can reduce testosterone production. Rest and recovery are crucial.
- Manage Stress:
- Lower Cortisol Levels: Chronic stress increases cortisol, a hormone that can lower testosterone. Practices like meditation, deep breathing, yoga, and mindfulness can help manage stress.
- Sleep Quality: Testosterone production is significantly affected by sleep. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to optimize hormone production.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Fat Loss: Excess body fat, especially around the belly, is associated with lower testosterone levels. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help boost testosterone.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption:
- Reduce Alcohol Intake: Excessive alcohol can lower testosterone levels, so limiting alcohol can help maintain healthy hormone levels.
- Consider Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT):
- If lifestyle changes do not significantly improve testosterone levels, testosterone replacement therapy may be considered. This can come in the form of injections, patches, gels, or pellets, and should only be prescribed and monitored by a healthcare provider.
- Avoid Environmental Toxins:
- Minimize Exposure to Endocrine Disruptors: Chemicals in plastics (e.g., BPA), pesticides, and other environmental toxins can negatively affect hormone levels. Reducing exposure to these can support healthy testosterone levels.
- Herbal Supplements:
- Certain herbs, like ashwagandha, fenugreek, and tribulus terrestris, have been studied for their potential to naturally boost testosterone levels. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before using supplements, as the evidence for their effectiveness can vary.
When to See a Doctor:
If you’re experiencing symptoms of low testosterone, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider. Blood tests can measure testosterone levels, and a doctor can recommend a treatment plan based on your individual needs.
By adopting a healthy lifestyle, focusing on nutrition, exercise, and managing stress, it’s possible to increase testosterone levels over time naturally. If necessary, medical treatments like TRT can be explored under the guidance of a healthcare professional.



 DailyMediCure
DailyMediCure