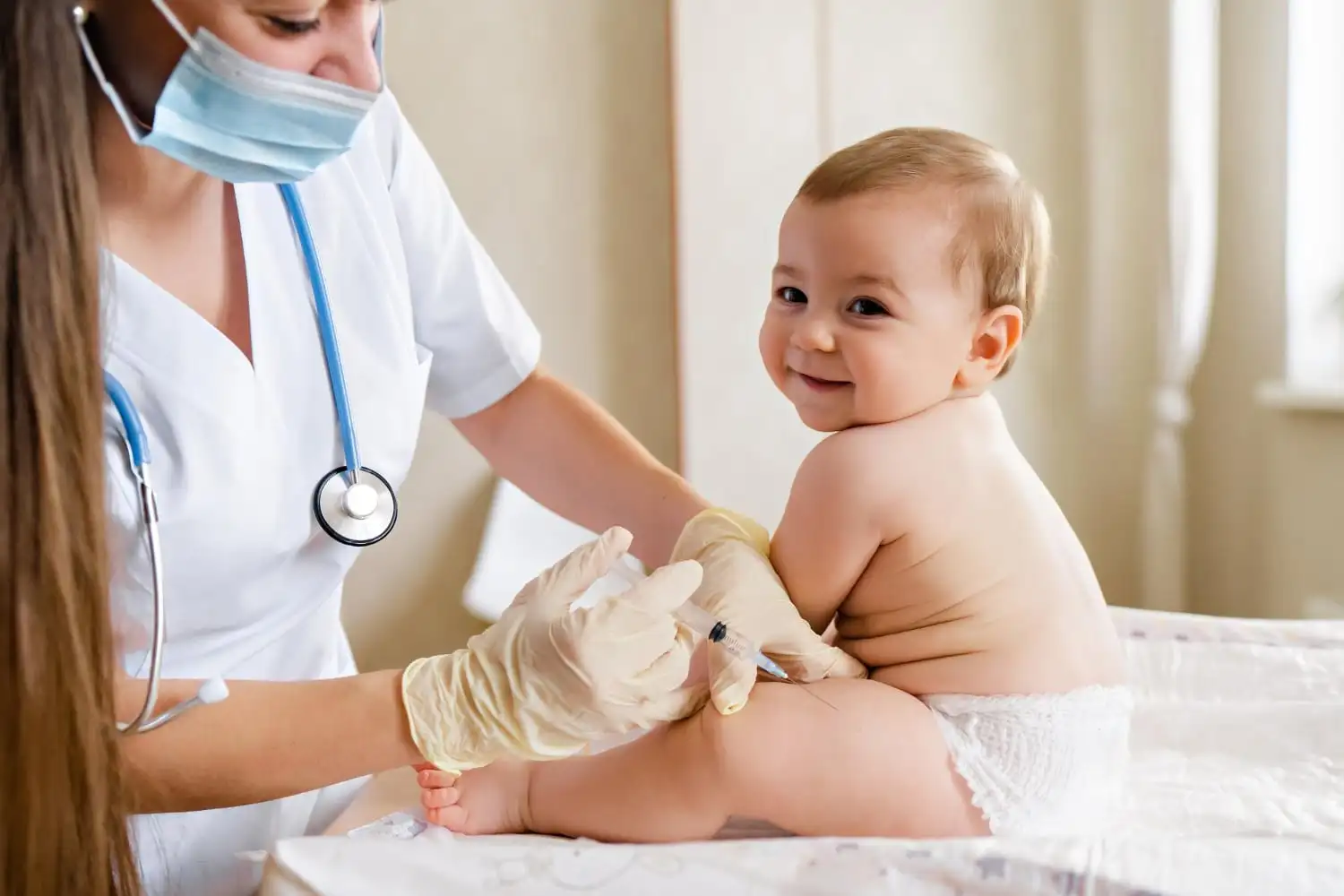
Newborn babies are typically given specific vaccination as part of national immunization programs to protect them from serious infectious diseases. The exact schedule may vary by country, but here is a general overview based on recommendations from organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC):
First Vaccination for Newborns:
- BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guérin):
- Purpose: Protects against tuberculosis (TB), especially severe forms like meningitis and disseminated TB.
- Timing: Given soon after birth, often within the first few days.
- Hepatitis B Vaccine (HBV):
- Purpose: Protects against hepatitis B, a viral infection that can lead to liver disease and cancer.
- Timing: The first dose is administered within 24 hours of birth.
- Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) (in some countries):
- Purpose: Protects against poliomyelitis (polio), a disease that can cause paralysis.
- Timing: Often given at birth, depending on the country\u2019s immunization schedule.
Vaccination Schedule for Infants and Children:
1–2 Months:
- Hepatitis B Vaccine (Second Dose):
- Given 1 month after the first dose.
2 Months:
- DTaP (Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis):
- Protects against diphtheria, tetanus, and whooping cough.
- IPV (Inactivated Polio Vaccine):
- Protects against polio.
- Hib (Haemophilus influenzae type b):
- Prevents bacterial infections that can cause meningitis, pneumonia, and epiglottitis.
- PCV (Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine):
- Protects against pneumococcal infections.
- Rotavirus Vaccine:
- Protects against severe diarrhea caused by rotavirus.
4 Months:
- Second doses of:
- DTaP
- IPV
- Hib
- PCV
- Rotavirus Vaccine
6 Months:
- Third doses of:
- DTaP
- IPV
- Hib
- PCV
- Rotavirus Vaccine (if a 3-dose series)
- Hepatitis B Vaccine (Third Dose):
6–18 Months:
- Influenza Vaccine:
- Annual vaccination begins at 6 months.
12–15 Months:
- MMR (Measles, Mumps, Rubella):
- First dose.
- Varicella (Chickenpox):
- First dose.
- Hepatitis A Vaccine:
- First dose.
- Booster doses of Hib and PCV.
15–18 Months:
- Booster dose of DTaP.
4–6 Years:
- Second doses of:
- MMR
- Varicella
- Booster doses of:
- DTaP
- IPV
Additional Considerations:
- Optional Vaccines (depending on region and risk):
- Meningococcal Vaccine: Protects against meningitis caused by meningococcal bacteria.
- HPV Vaccine: Administered later, around 11–12 years, to protect against cervical and other cancers.
- Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine: In areas where this disease is prevalent.
- Typhoid Vaccine: In regions with a high risk of typhoid fever.
Why Vaccination is Important:
Vaccines are essential for protecting children against life-threatening diseases. They not only protect the individual but also contribute to community immunity, reducing the spread of infections.
Would you like specific details for your country’s vaccination schedule? I can look it up for you!



 DailyMediCure
DailyMediCure